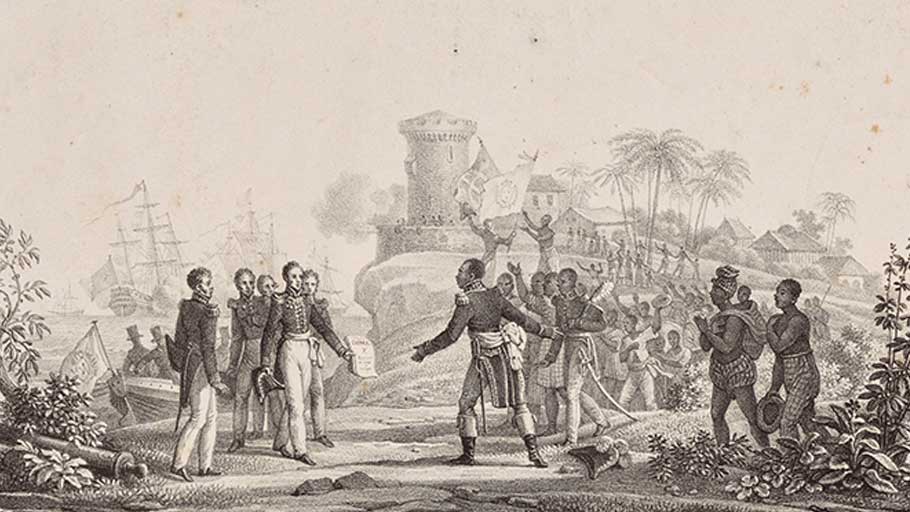The French have been exploiting black people for a long time.
Haiti officially declared its independence from France in 1804. In October 1806, the country was split into two, with Alexandre Pétion ruling in the south and Henry Christophe ruling in the north.
Despite the fact that both of Haiti’s rulers were veterans of the Haitian Revolution, the French had never quite given up on reconquering their former colony.
In 1814 King Louis XVIII, who had helped overthrow Napoléon earlier that year, sent three commissioners to Haiti to assess the willingness of the country’s rulers to surrender. Christophe, having made himself a king in 1811, remained obstinate in the face of France’s exposed plan to bring back slavery. Threatening war, the most prominent member of Christophe’s cabinet, Baron de Vastey, insisted,“ Our independence will be guaranteed by the tips of our bayonets!” 
A portrait of Alexandre Pétion. Credit: Alfred Nemours Archive of Haitian History, University of Puerto Rico.
In contrast, Pétion, the ruler of the south, was willing to negotiate, hoping that the country might be able to pay France for recognition of its independence.
In 1803, Napoléon had sold Louisiana to the United States for 15 million francs. Using this number as his compass, Pétion proposed paying the same amount. Unwilling to compromise with those he viewed as “runaway slaves,” Louis XVIII rejected the offer.
Pétion died suddenly in 1818, but Jean-Pierre Boyer, his successor, kept up the negotiations. Talks, however, continued to stall due to Christophe’s stubborn opposition.
“Any indemnification of the ex-colonists,” Christophe’s government stated, was “inadmissible.”
Once Christophe died in October 1820, Boyer was able to reunify the two sides of the country. However, even with the obstacle of Christophe gone, Boyer repeatedly failed to successfully negotiate France’s recognition of independence. Determined to gain at least suzerainty over the island – which would have made Haiti a protectorate of France – Louis XVIII’s successor, Charles X, rebuked the two commissioners Boyer sent to Paris in 1824 to try to negotiate an indemnity in exchange for recognition.
On April 17, 1825, the French king suddenly changed his mind. He issued a decree stating France would recognize Haitian independence but only at the price of 150 million francs – or 10 times the amount the U.S. had paid for the Louisiana territory. The sum was meant to compensate the French colonists for their lost revenues from slavery.
Baron de Mackau, whom Charles X sent to deliver the ordinance, arrived in Haiti in July, accompanied by a squadron of 14 brigs of war carrying more than 500 cannons.
Rejection of the ordinance almost certainly meant war. This was not diplomacy. It was extortion.
With the threat of violence looming, on July 11, 1825, Boyer signed the fatal document, which stated, “The present inhabitants of the French part of St. Domingue shall pay … in five equal installments … the sum of 150,000,000 francs, destined to indemnify the former colonists.”
French Prosperity Built on Haitian Poverty
Newspaper articles from the period reveal that the French king knew the Haitian government was hardly capable of making these payments, as the total was more than 10 times Haiti’s annual budget. The rest of the world seemed to agree that the amount was absurd. One British journalist noted that the “enormous price” constituted a “sum which few states in Europe could bear to sacrifice.” READ MORE